Learn the Names of Diamond Elements
Transforming a rough diamond into a faceted gem is a complex process. Specialized words help explain parts of a finished diamond and how they come together to make a beautiful stone. As diamonds are closely connected to engagement rings, wedding bands and other jewelry, one might see these terms while shopping. Here are some words and their meanings.
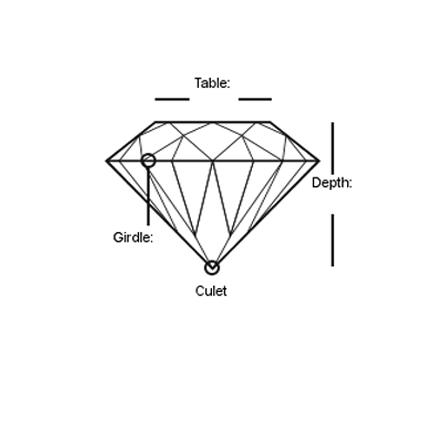 The table is the flat facet on the top of a diamond. Most diamond bands and other jewelry are set so the tables are the first thing a person sees. Brilliant cut diamonds are designed so light both enters and exits this facet, creating the sparkle diamonds are famous for. Step cut diamonds have broader tables than brilliants, allowing people to get a clearer view of the gem’s crystal.
The table is the flat facet on the top of a diamond. Most diamond bands and other jewelry are set so the tables are the first thing a person sees. Brilliant cut diamonds are designed so light both enters and exits this facet, creating the sparkle diamonds are famous for. Step cut diamonds have broader tables than brilliants, allowing people to get a clearer view of the gem’s crystal.
Crowns are the upper half of the diamond. It’s made of the table and other facets such as stars and kites. Round brilliant cut diamonds have strict standards on crown height, angle and so on to create ideal brightness. With diamond cuts with broader tables, their crowns may be smaller. Crowns also serve as prisms, helping to create the sparks of color inside the gem known as fire.
The girdle is the outermost edge of the diamond. It sits between the crown and the pavilion, and has a subtle effect on brilliance. Gemstones with overly thick girdles may have disrupted brilliance. However, diamonds with very thin girdles may be prone to damage. Cutters aim to keep the girdle narrow without being knife-edge thin.
Pavilions are the lower half of the diamond. In brilliant and mixed cut diamonds, they slope to a point, as do the facets on the pavilion. The angle of the pavilion in these jewels helps determine how bright the jewel will be. Step cut stones also angle down, though their facets sit in nested rows.
The culet is the bottom most facet on a diamond, sitting parallel to the table. Some cuts such as the emerald cut are designed to have noticeable culets. Others like the round brilliant use culets as an optional facet, to reduce the risk of chipping.





